Goods & Services Tax Law in India is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
In simple words, Goods and Service Tax is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. GST Law has replaced many indirect tax laws that previously existed in India.
GST is one indirect tax for the entire country.
So, before Goods and Service Tax, the pattern of tax levy was as follows:
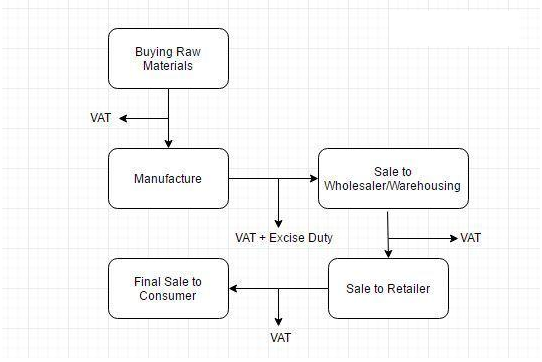
Under the GST regime, the tax will be levied at every point of sale. In case of interstate sales, Central GST and State GST will be charged. Intra-state sales will be chargeable to Integrated GST.
Now let us try to understand the definition of Goods and Service Tax – “GST is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that will be levied on every value addition.”
There are multiple change-of-hands an item goes through along its supply chain: from manufacture to final sale to the consumer.
Let us consider the following case:
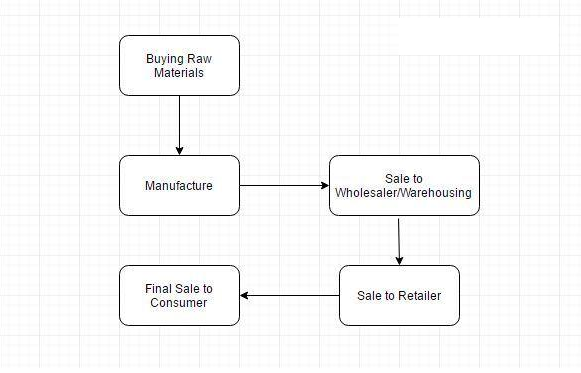
Goods and Services Tax will be levied on each of these stages, which makes it a multi-stage tax.
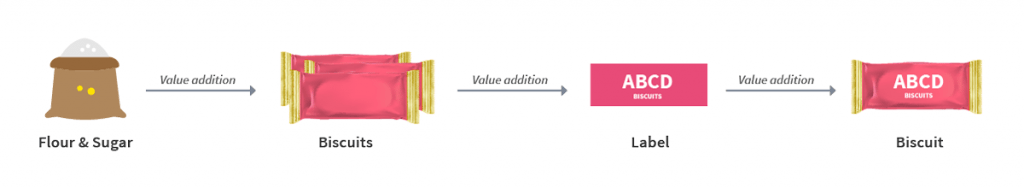
The manufacturer who makes biscuits buys flour, sugar and other material. The value of the inputs increases when the sugar and flour are mixed and baked into biscuits.
The manufacturer then sells the biscuits to the warehousing agent who packs large quantities of biscuits and labels it. That is another addition of value after which the warehouse sells it to the retailer.
The retailer packages the biscuits in smaller quantities and invests in the marketing of the biscuits thus increasing its value.
GST will be levied on these value additions i.e. the monetary worth added at each stage to achieve the final sale to the end customer.
Consider goods manufactured in Maharashtra and are sold to the final consumer in Karnataka. Since Goods & Service Tax (GST) is levied at the point of consumption, in this case, Karnataka, the entire tax revenue will go to Karnataka and not Maharashtra.
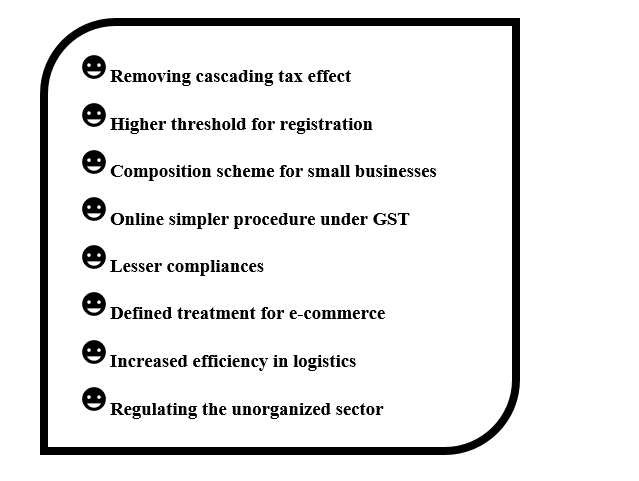
GST will mainly remove the Cascading effect on the sale of goods and services. Removal of cascading effect will directly impact the cost of goods. The cost of goods should decrease since tax on tax is eliminated in the GST regime.
GST is also mainly technologically driven. All activities like registration, return filing, application for refund and response to notice needs to be done online on the GST Portal. This will speed up the processes.
There are 3 taxes applicable under GST: CGST, SGST & IGST.
In most cases, the tax structure under the new regime will be as follows:
| Transaction | New Regime | Old Regime | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sale within the State | CGST + SGST | VAT + Central Excise/Service tax | Revenue will be shared equally between the Centre and the State |
| Sale to another State | IGST | Central Sales Tax + Excise/Service Tax | There will only be one type of tax (central) in case of inter-state sales. The Center will then share the IGST revenue based on the destination of goods. |
The dealer has to collect Rs. 6,000 as Goods and Service Tax. Rs. 3,000 will go to the Central Government and Rs. 3,000 will go to the Gujarat government as the sale is within the state.
Smart Step Financial offers a smooth process of GST registration. Our Professionals make your GST registration process hassle free and friendly. As digital India requires business global position GST need to be apply.
There are various GST returns need to be filed by GSIN holder. Smart Step financial helps to file GST returns within due dates relevant to the GTIN holder. Our qualified staff are well experience and accurate in their work.